Wednesday, October 16, 2013
Temperature Indicator
This temperature indicator indicates the temperature of a heat sink in high power circuits .In this temperature indicator, diode voltage drop in ambient temperature is used as reference level. Temperature is measured by a transistor mounted on a radiator or near power transistor controlled.T1 temperature sensor and voltage to the base - emitter is compared, through potentiometer P1, with the common point of reference in its D1 and R1. Transistor remains blocked as long as temperature remains below a certain level, which is set to P1. Base-emitter voltage of transistor will decrease by about 2 mV for a temperature increase of about 1 ° C.
When the emitter voltage of transistor voltage falls below the cursor P1, the transistor will go into conduction and D2 will light.The values of R1 and R2 are voltage dependence of Ub and relationships can be calculated:
R1 = [(Ub - 0.6) / 5] k, R2 = [(Ub - 1.5) / 15] k.
Temperature Indicator Schematic
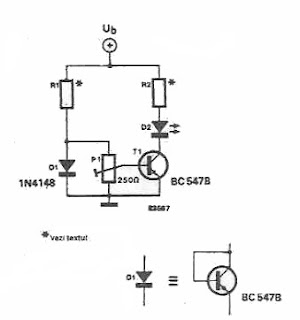
When the emitter voltage of transistor voltage falls below the cursor P1, the transistor will go into conduction and D2 will light.The values of R1 and R2 are voltage dependence of Ub and relationships can be calculated:
R1 = [(Ub - 0.6) / 5] k, R2 = [(Ub - 1.5) / 15] k.
Temperature Indicator Schematic

Related Posts : indicator,
temperature
Labels:
indicator,
temperature
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
No comments:
Post a Comment